Biography
Interests
Fariba Goudarzi1*, Robab Hassanvad Jamadi1, Faraham Ahmadzadeh2 & Hashem Yaghoubi3
1Department of Biology, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Iran
2Department of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Management, Environmental Sciences Research Institute, Shahid Beheshti University, Iran
3Department of biology, Ardabil Branch, Islamic Azad University, Ardabil, Iran
*Correspondence to: Fariba Goudarzi, Department of Biology, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Iran.
Copyright © 2018 Fariba Goudarzi, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
In the present study, the potential of the antimicrobial peptide of nisin has been studied in the
food (antibacterial activity) and pharmaceutical (anticancer activity) industries. This peptide can
be used both as a preservative and as a drug because the formation of pore in the membrane of
bacteria. In this study, the antimicrobial activity of nisin on reference strain of Staphylococcus
aureus ATCC 2592, a food pathogen, and the effect of this peptide on the gastric cancer cell
line (AGS) has been investigated. The effect of nisin on Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 2592 was
studied by the MIC method and it was observed that nisin has an antibacterial effect on this
bacterial strain. Study on cytotoxicity effect of nisin in different concentrations on the gastric
cancer cell line showed that with increased concentration and treatment time, more cytotoxicity
was observed.
Introduction
Bacteriocins are ribosomal peptides that produced by lactic acid bacteria; these peptides, with antimicrobial activity, are acid and heat resistance and easy to digest. According to the Kaiser and Montville theory, bacteriocins should have two properties: 1) Protein nature. 2) non-cytotoxic on cells that produce them [1]. Lantibiotics are a class of bacteriosins that are small and heat-resistant peptides and they have lantinone and methyl lanthanide amino acids in their structures. A subgroup of lantibiotics is an elongated, flexible, and positively charged peptide that creat pores in the membrane of target bacterial species, such as nisin [2]. Nisin have 34 amino acids {C143 H230 N42 O3} (Fig. 1); it has amphipathic structure with +4 charge, the N-terminal of this peptide is more hydrophobic than the C-terminal and produced by Lactococcus lactis
bacteria; Nisin have antimicrobial activity against a wide range of gram-positive bacteria, including Listeria monocytogenes and spore-producing bacteria such as Clostridium and Bacillus. Nisin creating pores in the membrane of bacteria and breaking the ionic gradient and result the death of the bacterial cell [3, 4], in addition it is preventing the cellular biosynthesis [5]. Because of the non-toxicity of this peptide, in 1969, FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) and WHO (World Health Organization) allowed it to be used as a food preservative [6]. Many studies have been done on nisin in the pharmaceutical and food industries [7, 8, 9, 10]. In this study, we have evaluated the anticancer (in the pharmaceutical industry) and antibacterial (in the food industry) effects of nisin.
Methods
There are various methods for collecting information that is often used in one or more methods for collecting
statistics and information based on the type and desires of scientific research. In general, data collection
methods are divided into two categories: library method and field method. In this research, both field and
library methods have been used to collect information. The research literature was compiled by a library
method and studied books, articles and searches on valid scientific websites. In this research, for analyzing the data obtained from the samples, both descriptive statistics and inferential statistics methods have been
used. SPSS and PLS software were used to perform these analyzes (6). In the descriptive section of the
demographic information operations, individuals will be sampled using the SPSS software process. Also,
tables and graphs containing mean, frequency, etc. will be used in this section. Structural Equation Modeling
(SEM) has been used in the inferential part by using PLS software.
Result and discussion
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of social capital on strategic performance with respect to
the moderating role of technological uncertainty. As previously mentioned, all dimensions of social capital
(capital, structural, and structural) affect the strategic performance, but the technological uncertainty in
these relations has no moderating role and failed to increase the impact of social capital dimensions on
The strategic performance will be effective. Now, according to the results, the present research proposals are
presented.
Output results obtained from SMART PLC 2 software are presented in the following table1
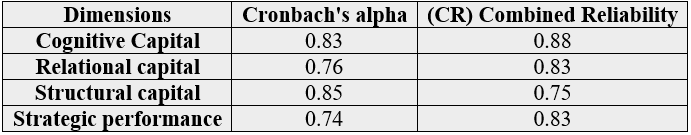
The increase of Cronbach’s alpha and combined reliability of the main research structures of 0.7, confirms the reliability of the model’s proper index.
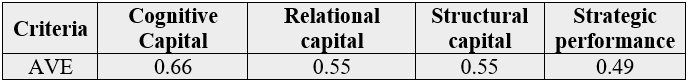
The values for the Average(AVE) of each structure are shown in Table 2. As you can see from this table, all AVE values are more than 0.4%, which confirms the suitability of the model’s consistent convergence.
Discussion
Given the relationship between social capital and strategic performance, active companies in the
pharmaceutical industry will pay great attention to improving the strategic performance of social capital and
its dimensions (capitalism, relational capital and structural capital); Use social capital indicators to evaluate
strategic performance and, by forming professional groups and associations in organizations, increase social capital in organizations. With regard to the relationship between capital and strategic performance, it is
suggested that corporate values be promoted in the organizations and that staff be moved towards common
goals. Also, all employees must be in the process of developing organizational norms and standards, and work
towards increasing the number of employees with each other in order to improve the strategic performance
of the organization. Regarding the relationship between relationship capital and strategic performance,
it is suggested that in organizations, relationships should be structured in such a way that relationships
based on cooperation and mutual trust are formed and cooperation is considered as an essential principle
for employees. Also, by forming teams in the organization, the field of cooperation of the team of staff, the
increase in criticism in the organization and the background of the commitment of more employees to the
organization.
Conclusion
All dimensions of social capital (capital, cognitive, and structural) affect the strategic performance, but
the technological uncertainty in these relationships has not a moderating role and could not be effective
in increasing the impact of social capital dimensions on strategic performance. Companies active in the
pharmaceutical industry will pay much attention to improving the strategic performance of social capital
and its dimensions (capitalism, relational capital and structural capital), and to use social capital indicators
to evaluate strategic performance, and by forming groups and associations Professional and specialized
organizations increase social capital in organizations.
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by Tamin Pharmaceutical Investment Company. We thank our colleagues from
Department of Strategic and also Dr. Saleh Rahimi who provided insight and expertise that greatly assisted
the research.
Bibliography

Hi!
We're here to answer your questions!
Send us a message via Whatsapp, and we'll reply the moment we're available!