Biography
Interests
Karimi, M., D.M.D.
Department of Paediatric Dentistry, Sepideh Dental Clinic, Iran
*Correspondence to: Dr. Karimi, M., Department of Paediatric Dentistry, Sepideh Dental Clinic, Iran.
Copyright © 2018 Dr. Karimi, M. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
The tooth is a part of the body’s health system. A tooth can directly or indirectly affect human health. Many diseases and even cardiovascular diseases in premature children are associated with dental diseases. Mothers with severe gum disease and acute gingival infections, the babies who give birth usually have a low weight. We do not feel these connections directly.
The possibility of tooth eruption can be seen from the age of five months, and the first primary teeth that will be erupted are the lower central incisor teeth. Needless to say, the delayed tooth eruption till the age of eight months should not worry the parents. The primary teeth dentition is completed in two to three years in each child. The dentition of the primary teeth is including four primary molars, and the rest are four anterior teeth in each arch. At the age of six, primary teeth starting to be replaced by their permanent teeth that we call the transitional stage, which is a very important stage in childhood.
The teeth are responsible for maintaining the proper spaces for the permanent teeth of the child. Not only they guide the growth of permanent teeth in the right position but also help the growth and development of face and dentitions, and affect growth, height, and shape of the face. Teeth are effective in a person’s beauty and sense of self-confidence. Teeth certainly help digest food in the first step. Healthy teeth that are free of caries provide a healthy environment for permanent teeth eruption.
Early loss of primary teeth, especially in the posterior area, will cause problems. Adjacent teeth may incline to the extracted area in which leads to more food accumulation and exposure to caries, and the tooth movement may prevent the permanent teeth eruption that is supposed to erupt in that space. As a result, the permanent teeth will not have the necessary space for the eruption. It will either remain impacted or will erupt in an abnormal path. Primary teeth are as important as permanent teeth. Only with special care from the primary teeth, we can expect to have permanent teeth to erupt in the right pathway. Therefore, parents need to be aware of children’s oral health and preserving them.
Primary Tooth Loss
In most children, deciduous teeth fall at a specific time. Sometimes, the primary teeth might lose earlier the
time than expected so that the cause of early tooth loss should be investigated.
Usually, at about 6 or 7 years old, due to the permanent teeth growth, the primary teeth get loose and the permanent teeth are replaced [1]. Of course, in some cases, there are some exceptions in which the eruption of permanent teeth occurs earlier, for example when genetic factors or teeth crowding are involved.
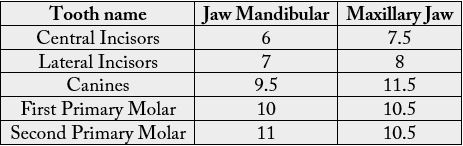
Time to Lose a Primary Tooth
The timetable shows it usually starts at the age of 6 and starts with two lower central incisors and then two
upper one [1]. Generally, at the age of 5 to 6, the kid’s teeth should be photographed and, with the dentist’s
decision, it should be determined which teeth have to be extracted so that the permanent teeth do not get
tangled.
It should be watched if the teeth are not lost at the age of 7; they may have erupted behind the lower primary teeth. This is the time that the expertise of a pediatric dentist would help to determine the right decision, and this will be detected by a simple PA radiograph. In fact, sooner or later of the teeth loss is not important. The important thing is that the permanent teeth are in their natural state because if the tooth does not erupt in its right pathway, it can grow tilted, or causes the tooth crowding.
Causes of Early Primary Teeth Loss
Early loss of deciduous teeth can damage the permanent teeth and can lead to abnormalities such as speech
disorders, crowding, inappropriate facial expressions, chewing problems, gum problems [2], and also increased
therapeutic costs in the future. Important factors are involved in this, which we briefly discuss.
The damage to the child’s mouth and teeth may happen due to the physical activities or playing in the
playground which causes loosen the tooth.
The extensive tooth caries can be one of the reasons which affect the early primary tooth loss. In this case,
most of the tooth’s structure has been destroyed, and the tooth cannot be preserved.
Some diseases, such as Fibrous Dysplasia [3], juvenile diabetes [4], Langerhans cell Histiocytosis [5], Cyclic
Neutropenia [6], Hypophosphatasia [7], Chediak - Higashi Syndrome [8], Rickets [9], Papillion-Lefevre
Syndrome [10] and Leukemia [10] are the most common diseases which cause the early primary tooth loss.
It is obvious that use of too many sweets and sugary contained materials can lead to early damage to of
the baby’s teeth. Preventing tooth loss requires a long-term commitment. In addition to poor oral hygiene
habits, eating a lot of candy, sweets, and other sugary snacks can lead to tooth loss.
Recommendations to Prevent Early Teeth Loss and Incorrect Permanent Teeth Eruption
There are some key points that parents have to remember if they don’t want their children to lose their tooth
too early.
1. To the extent possible, parents should prevent the child from using too much sugar and sweet substances.
2. Preventing from exposing to tooth decays by regular tooth brushing and keeping good oral hygiene.
3. Parents should regularly take their children to a dentist every six months to check the health of their teeth.
4. In the event of teeth caries, parents have to immediately begin to restore children’s teeth, especially if there
are interproximal caries. This problem not only causes pain, discomfort and the risk of early extraction but
also can lead to reduced space required for the permanent eruption of teeth.
5. If due to excessive caries, it is necessary to remove a primary tooth from the mouth, it is advisable to
consult with an orthodontist before taking any action, try to identify all aspects. In another word, whether
there is a need to maintain the empty space, and use of space maintainer or not.
6. Need to note that the crown of the teeth is formed at a time when the child is still in the fetal stages, so
the cases that the mother feeds from different nutrients during pregnancy is very effective on the strength
and formation of baby’s teeth.
7. The most important nutritious materials for strengthening of the baby’s teeth that are considered necessary
and effective including Calcium and Phosphorus which is often obtained through drinking milk; vitamin D
is present in large quantities in fish oil, fish meat, butter, cheese, and egg yolks; high levels of vitamin C are
seen in oranges and tomatoes. There are vegetables and other vitamins, including vitamins B and A which
are abundant in liver, dairy, cereals, beans, and grains. It is better for pregnant women to be aware of the
properties of these materials to the extent necessary and adequate to feed them.
8. Bacteria play an important role in the formation of tooth decays and because the decay is a contagious
disease, hence, when there are teeth decays in mother’s mouth, this can be transmitted to the baby. If a mother
can restore all the teeth decays before pregnancy, the child’s exposure to tooth decays can dramatically be
reduced.
9. After the baby is born, parents try to clean gums and new teeth with a damp pad after drinking milk or
eating food. They also can use a finger brush with water. After the age of 3, the brushing can be accompanied
with a small amount of toothpaste. IF the parents are worried about children’s tooth decays at this period,
oral hygiene should be kept in the best condition.
10. Apply fluoride mouthwashes and use antibacterial mouthwashes when needed. Since the age of two, we
can start fluoride therapy to give the strength to their teeth. After age 3, use of preventive dentistry such as
the application of fissure sealants for teeth D and E should be mandatory. After the eruption of first molars,
fissure sealants also have to be used. Therefore, to prevent the teeth decays, their oral hygiene must be under
the supervision of the parents, and the routine dental check-up should be done on time.
Bibliography

Hi!
We're here to answer your questions!
Send us a message via Whatsapp, and we'll reply the moment we're available!