Biography
Interests
Jordi Calvo Sanz1,2*, Manel Torelló Vilar1,3 & Pol Monné Cuevas1,2
1Physioterapist in Hospital and Center for Prevention and Rehabilitation Asepeyo St Cugat del Vallès. Barcelona, Spain
2Professor of Physiotherapy, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universitat Internacional de Catalunya
(UIC Barcelona), St.Cugat del Vallès, Barcelona, Spain
3Associate Professor Physiotherapy Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), Barcelona, Spain
*Correspondence to: Dr. Jordi Calvo Sanz, Department of Rehabilitation Hospital and Center for Prevention and Rehabilitation Asepeyo & Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences. Universitat Internacional de Catalunya (UIC Barcelona) St Cugat del Vallès, Barcelona, Spain.
Copyright © 2019 Dr. Jordi Calvo Sanz, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Introduction
Achilles tendinopathy especially in chronic phase is characterised by pain, swelling and loss of functionality
of Achilles tendon. It is a pathology developed by overuse and demand on the tendon being frequent in sports
as running or jumping [1]. There is insufficient evidence about which is the most appropriate conservative
treatment. Although, there is consensus in current evidence in use of conservative treatment before surgical
treatment, current evidence endorses the use of eccentric work with extracorporeal shockwaves therapy
ESWT [2].
Material and Methods
Bibliographic review in Databases (BBDD) in the period 2005‐2019. We looked for that terms: shockwave
and tendinopathy and achilles. The databases consulted have been: Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane Plus,
Pubmed.
Several random clinical assays were found and analyzed : [3-5] of the type wave of electromagnetic crash; [6-9] of the type of wave of piezoelectric crash and 3 clinical assays without group control: [10] of the electromagnetic type, [11] of the type electrohydraulic, of the pneumatic radial type [12] and also the results of some systematic reviews.
Results
At a systematic review of the 2015 about the application of ESWT in chronic achilles tendinopathy in a group
of 46 patients eccentric exercise and “wait and see”, concluded that the ESWT and /or the eccentric exercise
was an excellent option on the ache and the functional improvement on chronic calcified tendinopathy and
the chronic tendinopathy of the half portion [13].
Another sistematic review Yu.H et al, (2016) asserts on the benefits of ESWT in combination with physical agents‐therapeutic at inferior extremities and the eccentric work [14].
At the RS of Wiegerinck J. et al, (2013) based on 14 articles of the treatment of achilles tendinopathy where compared several treatments with ESWT, eccentric, surgery and injections; ESWT was effective at insertional non calcified achilles tendinopathy, but the patients subjected at surgery expressed to be more satisfied [15].
In the systematic review by Mani‐Babu et al, (2015) on the effectiveness of ESWT in several lower limb tendinopathies that collect data in 20 surveys, the reference in Achilles tendinopathy concludes that shortterm insertion type it is superior in eccentric and in that it is of the non‐insertional type they are effective combined with eccentric and superior to other treatments [16].
Reviewing the therapeutic algorithm in Achilles tendinopathy proposed by Rees J et al (2009), we can appreciate the place that ESWT would occupy together with other therapeutic proposals [17].
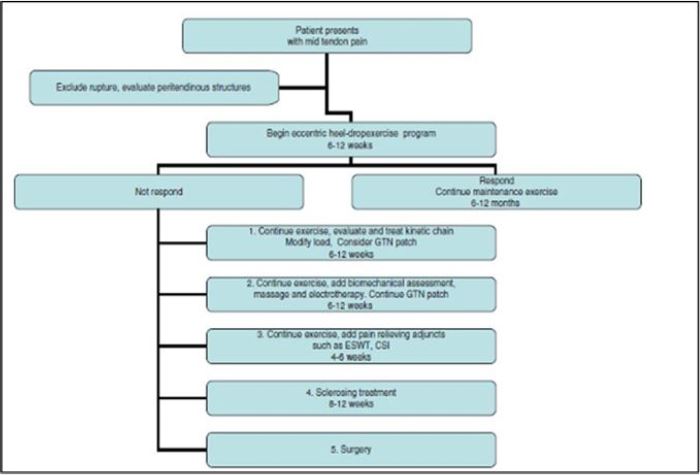
Conclusions
The combination of the therapy ESWT with other therapies in the conservative boarding of at chronic
phase (> 6 months of evolution ) is more effective that one of them individually. The eccentric exercises are
less effective compared with the combination of eccentric exercises more the app of waves of crash of low
energy analysing the variables : ache and improvements at the functional scale VISA‐A Questionnaire [7]
(Picture 1).
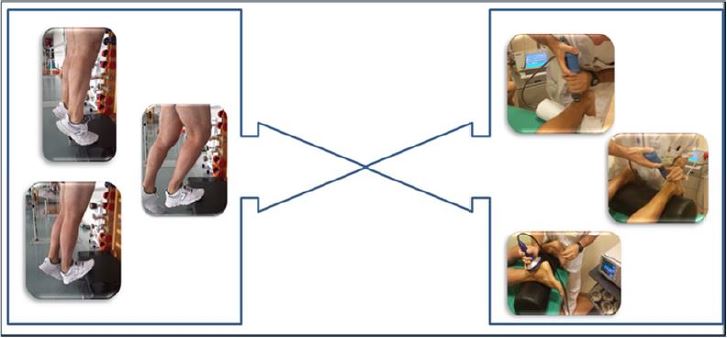
Bibliography

Hi!
We're here to answer your questions!
Send us a message via Whatsapp, and we'll reply the moment we're available!